[最も共有された! √] exocrine glands 196315-Exocrine glands
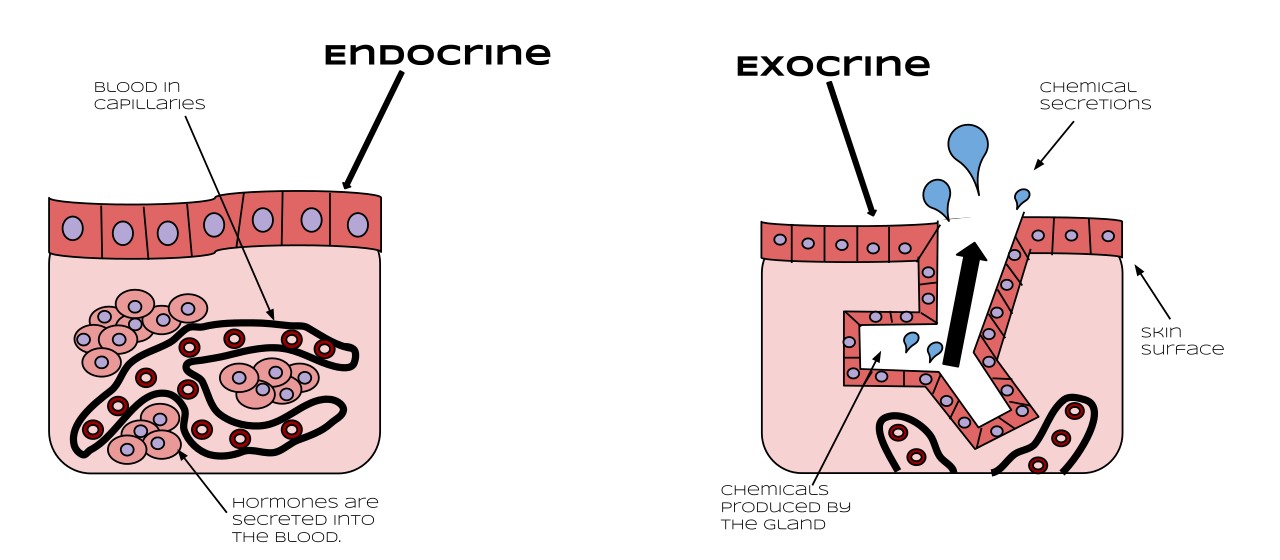
These glands form part of the endocrine system and information on them is included in this website There is another type of gland called an exocrine gland (eg sweat glands, lymph nodes) These are not considered part of the endocrine system as they do not produce hormones and they release their product through a ductThe glands are structures formed by epithelial cells of secretory function , in the glands are synthesized substances that are released into the bloodstream ( endocrine glands ) or inside cavities of the body or its surfaces ( exocrine glands ) All the glands of the body are formed by an invagination growth of an epithelial surface Exocrine glands are glands that are responsible for substances that pass through a network of ducts and are eventually released into an internal or external surface These surfaces include the mammary glands, sebaceous glands, and mucusproducing glands Examples of these glands include sweat glands, salivary glands, and digestive glands
1
Exocrine glands
Exocrine glands-Exocrine Glands Structural classification Functional classification Glands in the human body are classified as exocrine or endocrine The secretions of exocrine glands are released through ducts onto an organ ' s surface, while those of endocrine glands are released directly into the blood The secretions of both types of glands are carefully regulated by the body Exocrine glands are note considered part of the endocrine system These glands create a wide variety of products and excrete them through a network or ducts The products that are created in the




Pin On School
Exocrine glands These are glands possessing ducts and are lined along the insides of the gastrointestinal tract, in the stomach as well as the intestines They secrete ions, water and make substances like sweat, saliva, digestive juices Summary The major difference between the endocrine and exocrine gland is that, an endocrine gland is missing ducts and stays as blocks of tissue Endocrine gland secretes chemical substances directly to the blood stream, while exocrine gland secrets its product into aAdditionally, the term "gland" does not necessarily mean that the organ is part of the endocrine system For example, sweat glands, salivary glands, glands in mucus membranes, and mammary glands are called exocrine glands, because they secrete substances other than hormones and because they secrete the substances into ducts, not directly into the bloodstream
Unicellular at times as in goblet cells that produce mucus Gland size in endocrine glands Large in size, seen with the eye;Exocrine Glands Send chemicals/signals outside bodycuticle layer They may be single cells or small aggregates of secretory cells;Exocrine glands in plant life produce water, sticky protective fluids, and nectars The substances necessary for making birds' eggs, caterpillar cocoons, spiders' webs, and beeswax are all produced by exocrine glands Silk is a product of the silkworm's salivary gland secretion
Exocrine glands are sweat, salivary, mammary, ceruminous, lacrimal, bileproducing glands, prostate, sebaceous, and mucous Popular Products Hormones are one best example of the products of the endocrine Enzymes are one of the best examples of the products of the exocrineInflammation of the pancreas begins in the microscopic exocrine glands of the pancreas and progresses to macroscopic changes such as enlarged or atrophic pancreas, ductal abnormalities, cysts, and later calcifications, which indicates chronic pancreas inflammationExocrine Glands Exocrine glands have ducts that carry their secretory product to a surface These glands include the sweat, sebaceous , and mammary




Endocrine System Function Of Endocrine System Endocrine Glands




Epithelial Gland Types Endocrine Exocrine Sweat Glands Stock Illustration Illustration Of Deliver Illustrations
Exocrine glands consist of duct portion and a glandular portion where the glandular portion is branched The glandular portion consists of either a round or elongated cluster of cells These cells are different types and produce various substances The most common cells include serous cells which excrete protein and mucous cells which produceDefinition of exocrine gland a gland (such as a salivary gland or part of the pancreas) that releases a secretion external to or at the surface of an organ by means of a canal or duct First Known Use of exocrine gland Exocrine glands consist of two main parts, a secretory unit and a duct The secretory unit consists of a group of epithelial cells, which release their secretions into a lumen A duct is lined with epithelium and is involved in transporting the secretions from the secretory unit to an epitheliumlined surface



7 Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands With Examples Viva Differences



File Endocrine Vs Exocrine Svg Wikimedia Commons
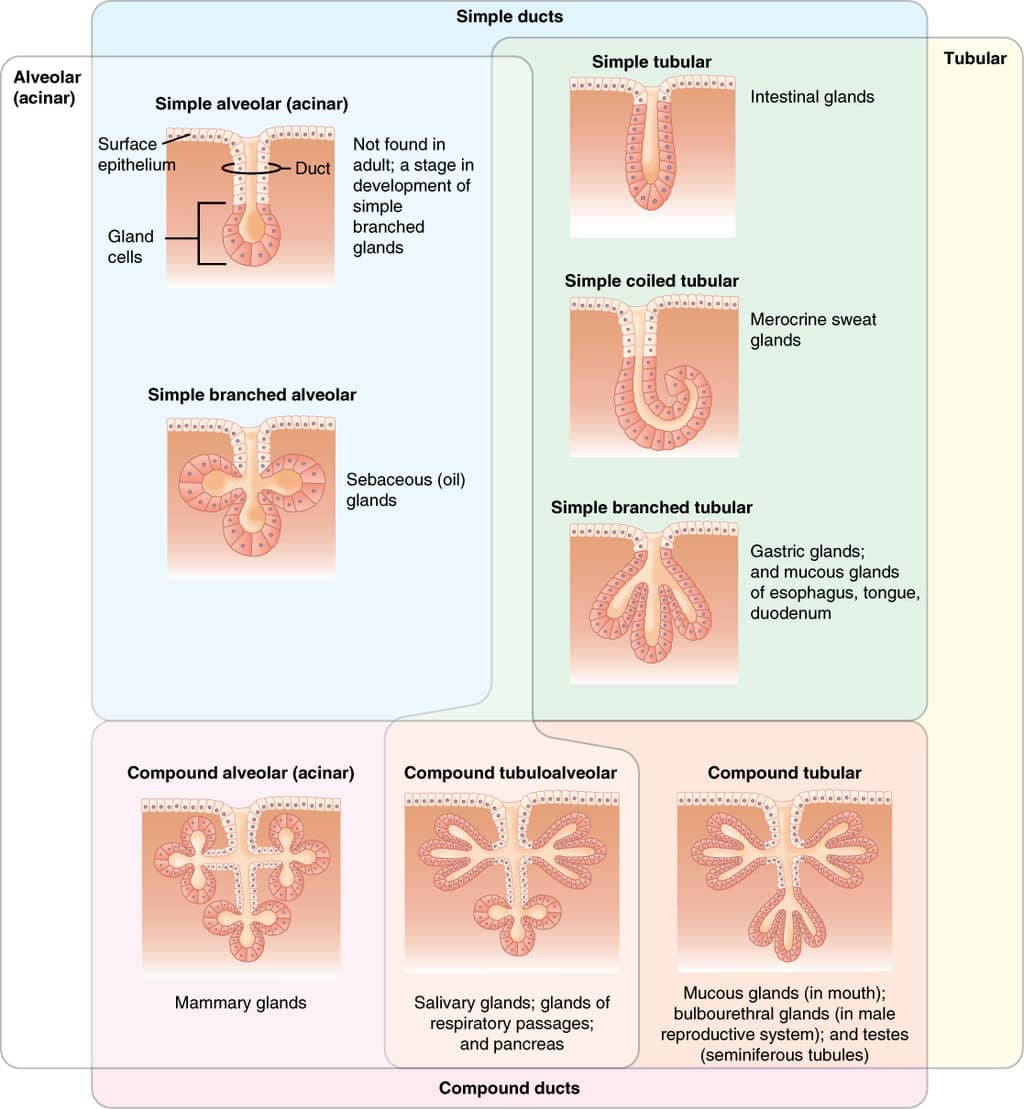
Exocrine glands are glands which produce secretions destined for the surface of an organ, as opposed to endocrine glands, which secrete compounds into the bloodstream Some examples of these glands include the mammary glands, sweat glands, and saliva glands Some glands are both endocrine and exocrine in nature, secreting hormones into theThey can either be simple or compound Simple glands these have a single, unbranched ductEndocrine glands are the glands that secrete hormones without ducts, while exocrine glands secrete hormones through ducts Read on to explore more differences between the two Secretory products released directly into the bloodstream, eventually reaching the target organ




Differences Between Exocrine And Endocrine Glands Online Science Notes




Exocrine Glands Meaning Pronunciation Origin And Numerology Nameslook
Gland size in exocrine glands Small in size; These glands essentially secrete enzymes, hormones, and other essential fluids Different Types of Glands in the human body Exocrine secretion is sent out of the gland while the secretion of the endocrine glands is collected by the blood capillary Exocrine glands These glands secrete their contents into a particular region of the bodyExocrine glands are composed of a cluster of secretory cells which collectively form an acinus (plural = acini) The acini are surrounded by a basement membrane and are held together by tight junctions between secretory cells The secretory cells possess a highly developed ER and golgi network for material secretion and are rich in mitochondria



Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Definition Types Features Functions



Exocrine Gland Stock Illustrations 157 Exocrine Gland Stock Illustrations Vectors Clipart Dreamstime
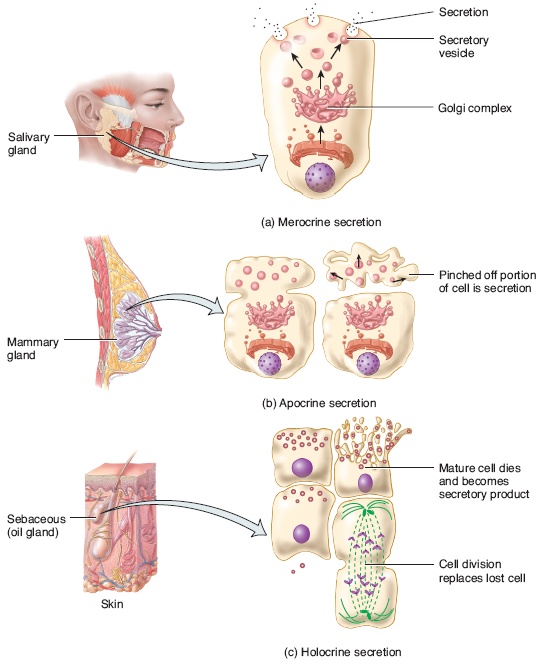
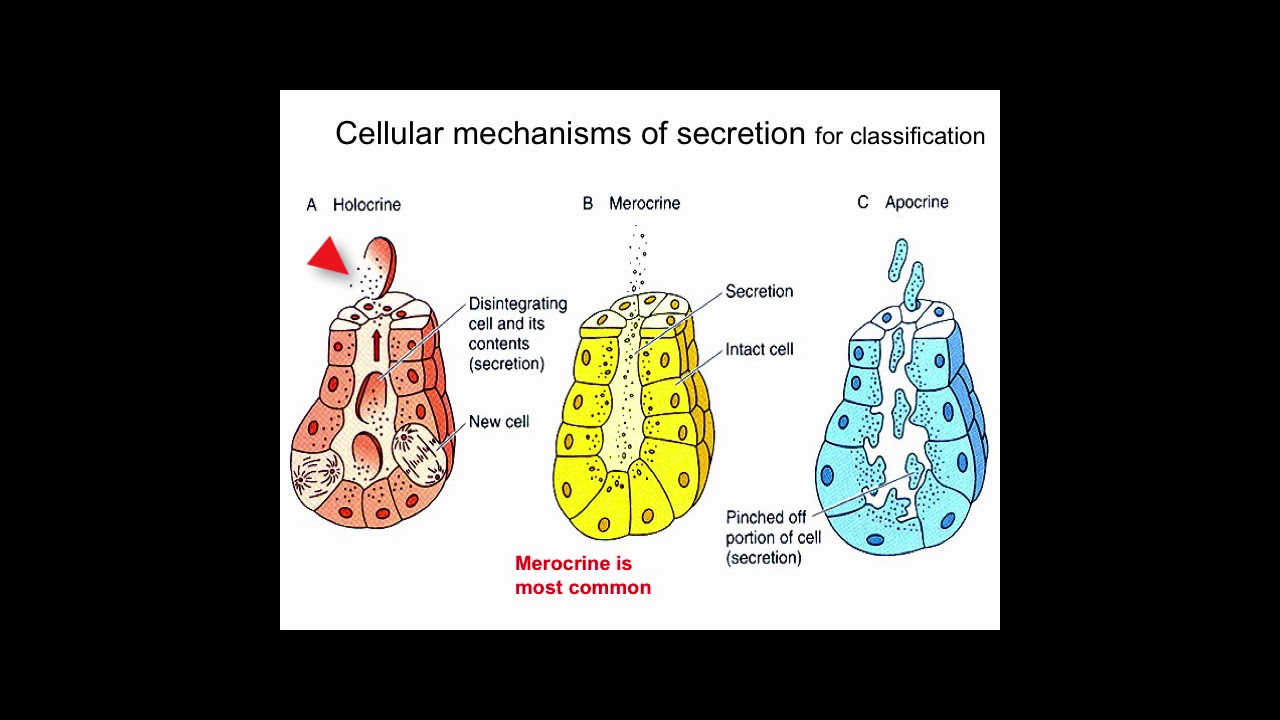
Define exocrine glands exocrine glands synonyms, exocrine glands pronunciation, exocrine glands translation, English dictionary definition of exocrine glands Sweat glands and other glands that release their products through ducts to a surface or cavity Three types of exocrine glands can be identified based on the mode of secretion merocrine glands, apocrine glands, and holocrine glandsThe merocrine glands secrete their own cellular products The apocrine glands gather the cellular products on the top surface of each cell in the gland and later forms the gland's lumen All cells of the gland are involved in the secretion in holocrine glandsThe study of endocrine glands is called endocrinology Thomas Addison is known as 'The Father of Endocrinology' Types are Endocrine and ExocrineEndocrine glands are the ductless glands secreting hormones directly into the bloodstream and control longterm activity of target organ They control, coordinate and influence various physiological activity of the body




Exocrine Gland Illustration Stock Image C039 2495 Science Photo Library



15 Types Of Glands In Human Body Their Functions
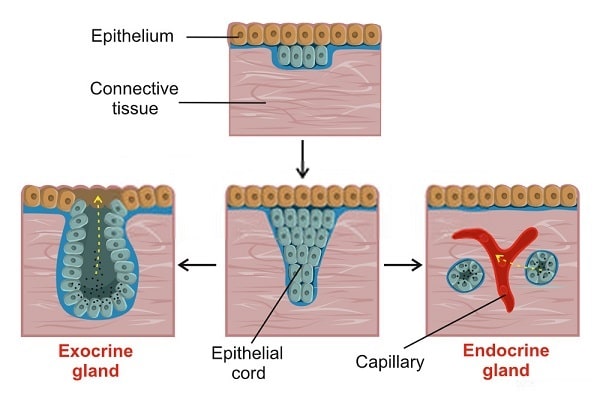
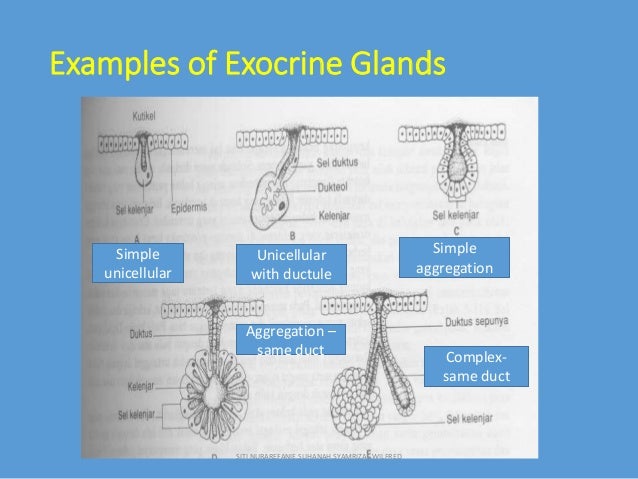
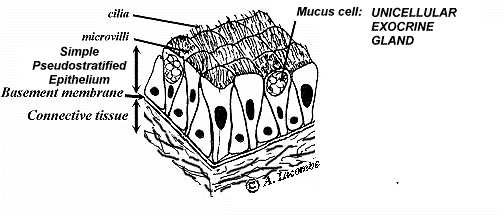
A unicellular gland, the simplest exocrine gland, is a single secretory cell that remains in the epithelium where it forms Although other examples exist, the most common unicellular exocrine gland is the goblet cell, demonstrated here Goblet cellsExocrine glands, classified by secretion product which is viscous, slimy and rich in large glycosylated proteins and some carbohydrates most common secretion is mucinogen (glycoprotein precursor) that forms mucin when hydrated, which is a component of mucus Exocrine glands can be classified by their mode of secretion and the nature of the substances released, as well as by the structure of the glands and shape of ducts Merocrine secretion is the most common type of exocrine secretion The secretions are enclosed in vesicles that move to the apical surface of the cell where the contents are
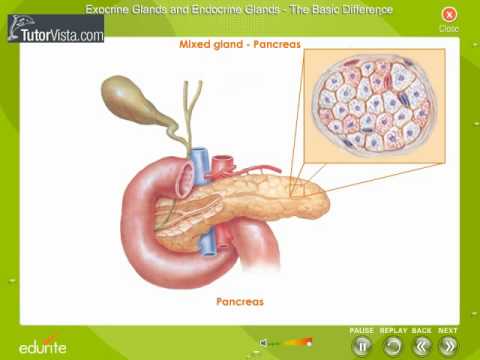



Exocrine Gland And Endocrine Glands Youtube




Significance Of Endocrine Vs Exocrine Glands Total Assignment Help
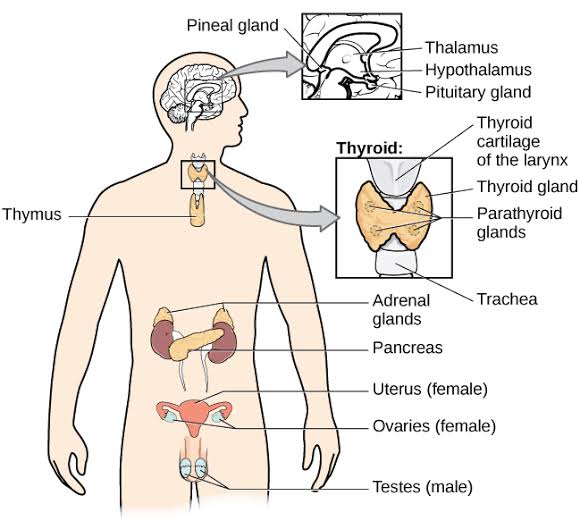
Description and function In gland Exocrine glands (eg, salivary, sweat, digestive) discharge their products through ducts Read More In integument Skin glands of the skin are all exocrine, that is, they secrete their products, usually through ducts, to the epidermal surfaceExocrine Glands Exocrine glands have ducts and they secrete onto a surface examples of exocrine glands are sebaceous and sweat glands (in the skin), salivary glands (oral), Brunner's glands So, we have covered their basic structure and function in tissue types, and we have looked at several examples of exocrine glands in other topics An exocrine gland is a gland that secretes its products into ducts that lead to the target tissue Examples of exocrine glands are sweat, salivary, sebaceous, mucous gland Examples of endocrine glands are pituitary gland, ovaries, testes, thyroid gland, adrenal glands



Animal Tissues Epithelial Tissue Glands Atlas Of Plant And Animal Histology




Exocrine Gland Types Artwork Stock Image C008 9643 Science Photo Library
Organs ie thyroid, pancreas Secretions released in exocrine glands secretions areExocrine glands are glands that discharge secretions by means of a duct, which opens onto an epithelial surface (a tissue that covers the external surface of the body and lines hollow structures inside the body) Exocrine glands include the sweat, sebaceous, and mammary glands, and the glands that secrete digestive enzymesOr can be complex glands Exocrine glands are generally of ectodermal origin and are widely scattered over the insect Examples of exocrine glands A Simple unicellular gland B Unicellular cell with ductule cell C



Exocrine Gland Mechanisms




Exocrine Gland Structure Physiology Americorps Health
Glands are collections of secretory epithelial cells This article discusses the structure of the two main types of glands ( exocrine and endocrine ) Exocrine glands secrete onto a surface and possess 'ducts' lined with epithelium;NCI's Dictionary of Cancer Terms provides easytounderstand definitions for words and phrases related to cancer and medicine A gland is a functional unit of cells that works together to create and release a product into a duct or directly to the bloodstream Two principal types of glands exist exocrine and endocrine The key difference between the two types is that, whereas exocrine glands secrete substances into a ductal system to an epithelial surface, endocrine




Difference Between Exocrine Glands And Endocrine Glands
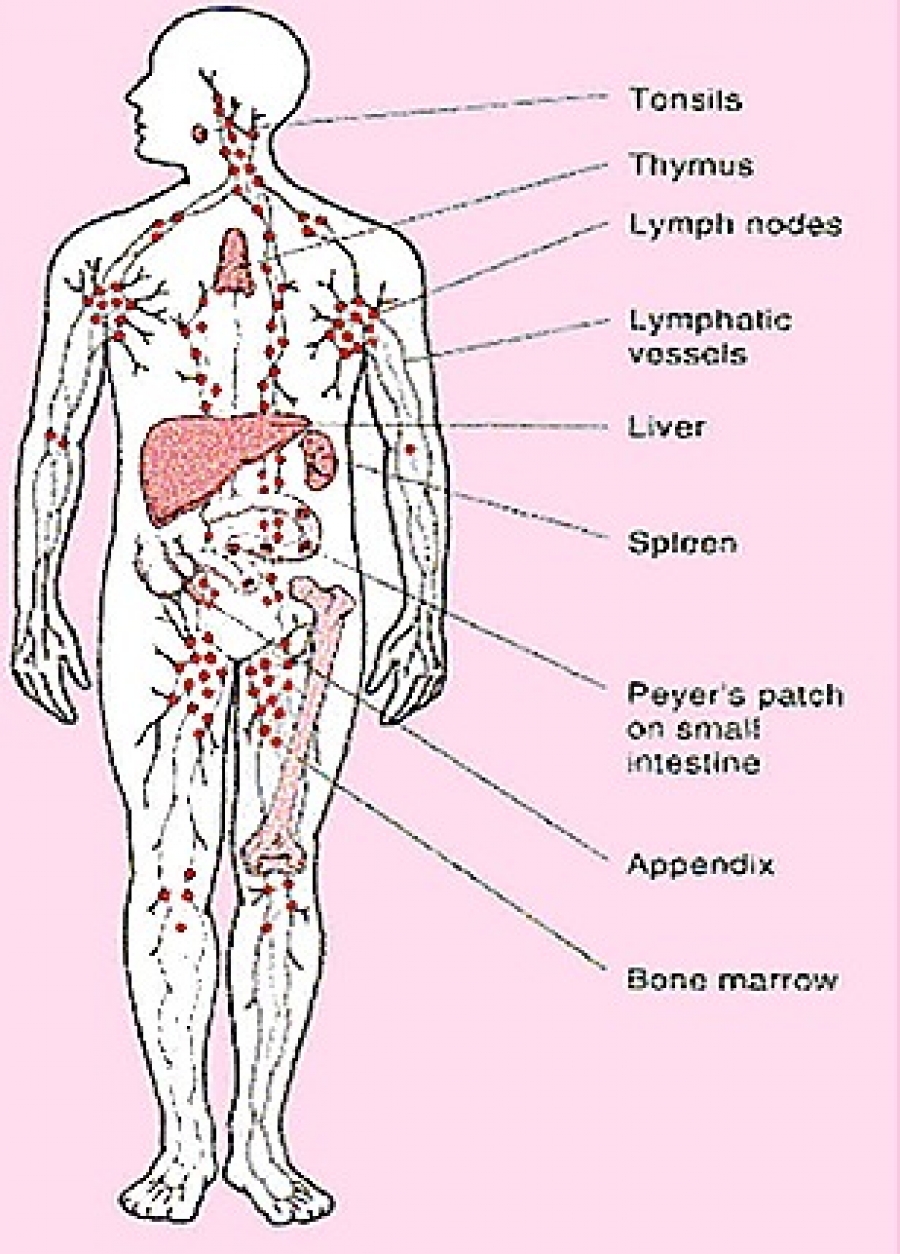



Important Exocrine Glands Present In Animals Their Position And Functions
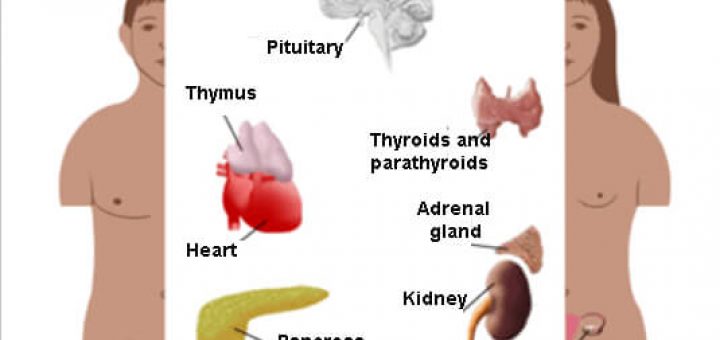
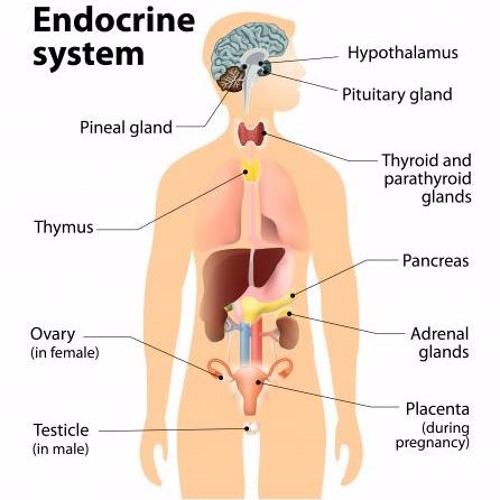
Examples of Endocrine and Exocrine Glands By glands It is understood as an organized and hyperspecialized set of cells whose function in the body is the secretion of certain chemical substances such as hormones, lipids or mucus For instance pituitary, thyroid, sweat glands According to the way they have to lead these secreted substancesDefine exocrine gland exocrine gland synonyms, exocrine gland pronunciation, exocrine gland translation, English dictionary definition of exocrine gland n A gland, such as a sebaceous gland or sweat gland, that releases its secretions to the body's cavities, organs, or




Exocrine And Endocrine Glands




The Location Of The Most Commonly Occurring Exocrine Glands In Ants Download Scientific Diagram




Distribution Of Connexins In Rat Endocrine And Exocrine Glands As Download Table




Integumentary System Description Your Guide To Healthy Living




Prostate An Exocrine Gland Of The Male Reproductive System Within It Sits The Urethra Coming From The Bladder Which Is Called The Prostatic Urethra And Which Merges With The Two Ejaculatory Ducts



Significance Of Endocrine Vs Exocrine Glands Total Assignment Help
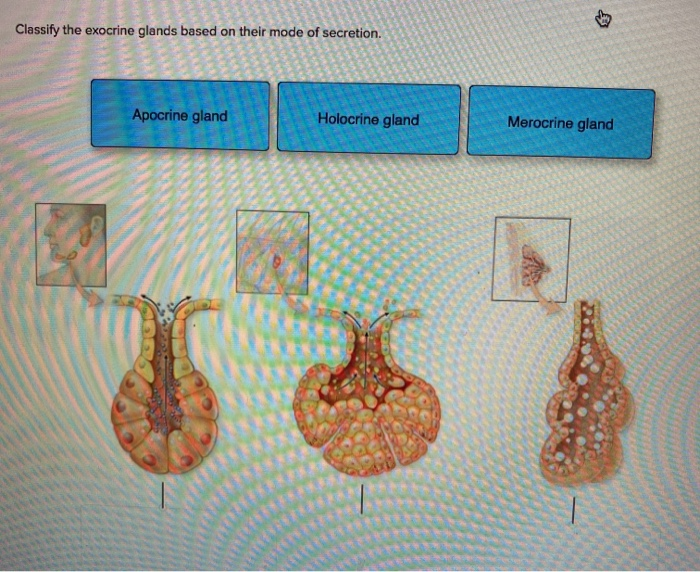



Solved Classify The Exocrine Glands Based On Their Chegg Com




Formation Of Endocrine And Exocrine Glands From Epithelial Sheets Diagram Quizlet



Key Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands You Should Know New Health Advisor



1



Epithelia The Histology Guide




Scielo Brasil Exocrine Glands Of Schwarziana Quadripunctata Hymenoptera Apinae Meliponini Exocrine Glands Of Schwarziana Quadripunctata Hymenoptera Apinae Meliponini




Glands In The Human Body And Their Functions



Structure Of Glands Exocrine Endocrine Histology Teachmephysiology



Exocrine And Endocrine Glands




Exocrine Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock



Definition Exocrine Gland



1




What Is The Difference Between Endocrine Exocrine And Paracrine Glands Lorecentral



Difference Between Exocrine Glands And Endocrine Glands Diferr




Exocrine Gland Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Solved Which Of The Followings Is The Largest Exocrine Gland In Hum



Al S Tutorial Histology Epithelium Glandular Epithelia




Exocrine Glands Vs Endocrine Glands What Is The Difference Diffzi



1




Expression Of Ikkb In Stratified Epithelia And Exocrine Glands Of Download Scientific Diagram




5 1 Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Secrete Substances Composed Of Epithelial Tissue Exocrine Glands Connect To Surface With A Duct Epithelial Tube Endocrine Ppt Download




Lecture 15 Endocrine Exocrine Glands In Insects Youtube



Endocrine Exocrine Glands




Endocrine System 1 2 Morphological Differences Exocrine Glands




Novel Exocrine Glands In The Foreleg Coxae Of Discothyrea Ants Sciencedirect




Exocrine Glands




Pin On School




Multicellular Exocrine Gland 1 Pharmedical Notes Facebook




Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Differences Function Terms Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
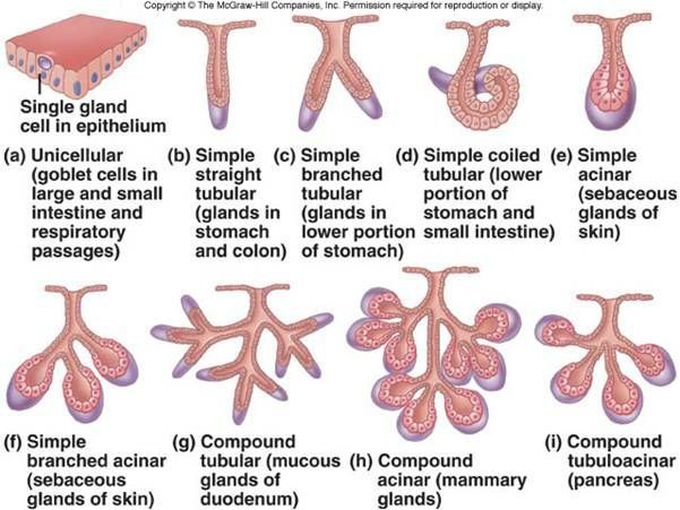



Types Of Exocrine Glands With Their Locations



Exocrine Glands By Kasia Plewa



Classification Of Exocrine Glands Type Of Secretions Produced
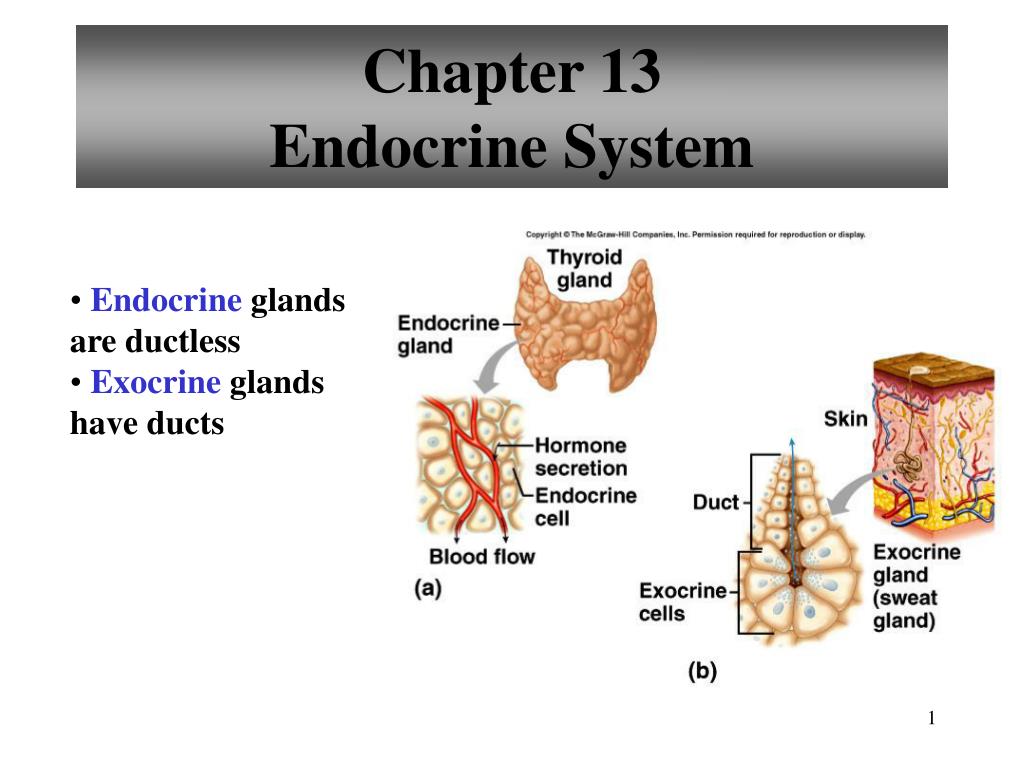



Ppt Chapter 13 Endocrine System Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id



Plos One Queen Specific Exocrine Glands In Legionary Ants And Their Possible Function In Sexual Selection
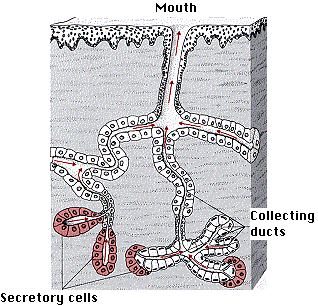



Exocrine Glands




Anatomy Of An Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Stock Illustration Download Image Now Istock




Exocrine Gland An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
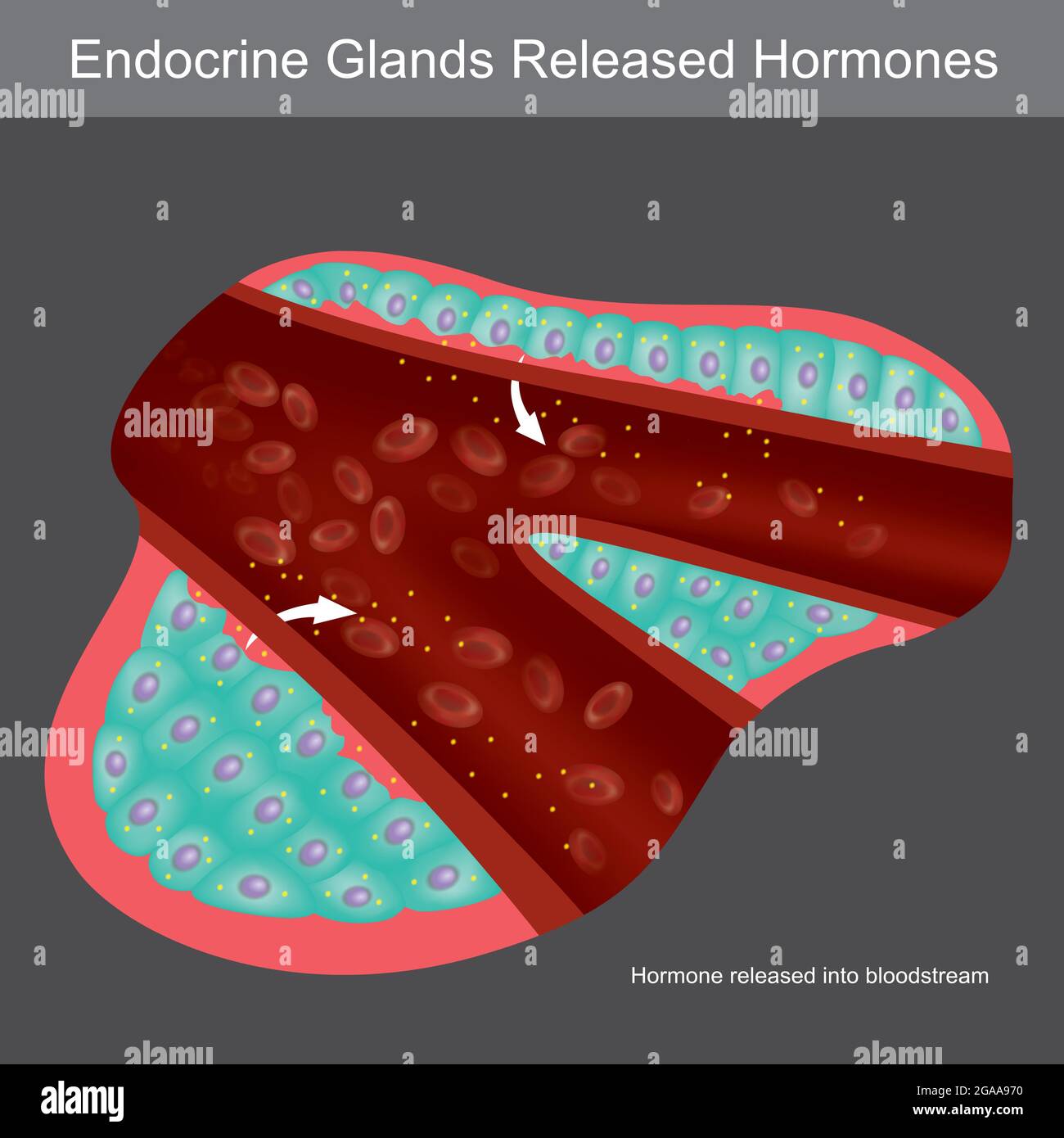



Exocrine Glands High Resolution Stock Photography And Images Alamy




Mixed Exocrine Gland Stock Photo Download Image Now Istock
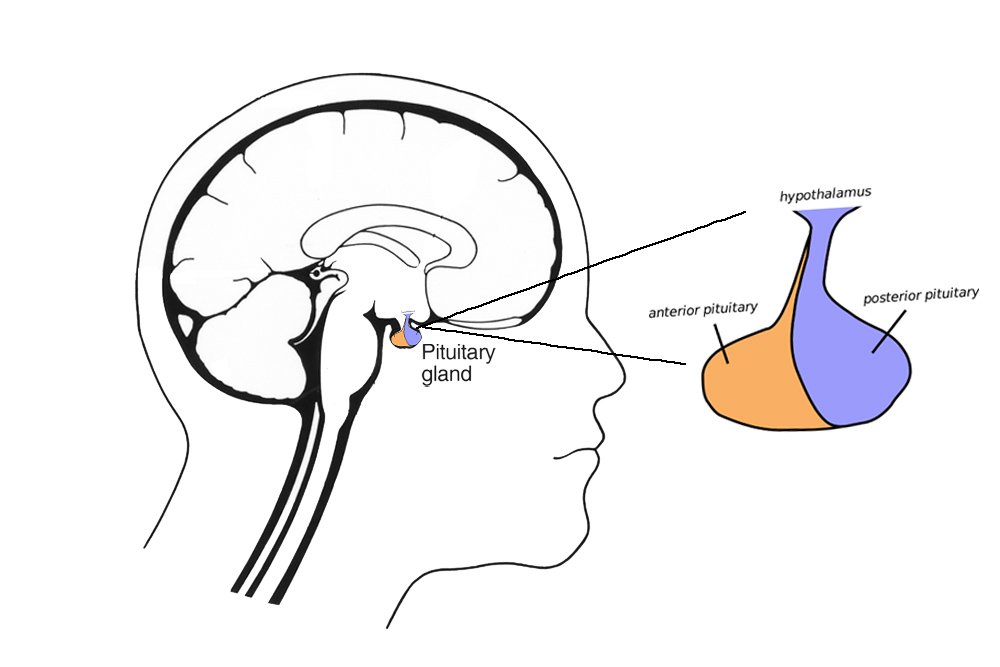



Endocrine Vs Exocrine Gland Defintion Functions And Differences
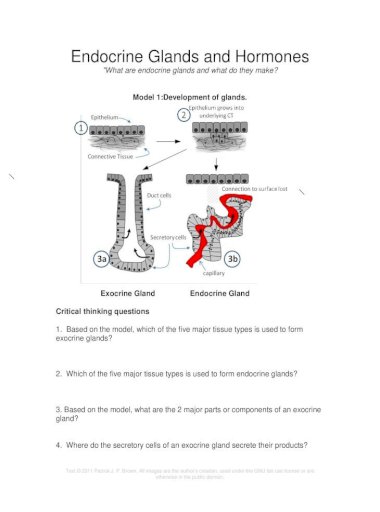



Endocrine Glands And Hormones Edl Glands And Hormones What Are Endocrine Glands And What Do They




Exocrine Gland Wikipedia




Table 1 From Occurrence And Structural Organization Of The Exocrine Glands In The Legs Of Ants Semantic Scholar




Current Approaches To Exocrine Gland Dysfunction As A Consequence Of Dils Download Table




Exocrine Vs Endocrine Glands Ppt Download



1




Epithelial Glands Basicmedical Key




Exocrine Glands Jacobo Pena A By Jacobo Pena Arredondo On Genially



Is The Parathyroid An Endocrine Gland Are Sweat Glands Endocrine Glands Socratic




Endocrine Exocrine Glands Structure Flashcards Quizlet




Exocrine Glands Bioninja




Overview Of Exocrine Gland Physiology Pancreatic And Salivary Glands The Gastrointestinal System Medical Physiology 3rd Edition



Exocrine Glands Science Online




Introduction To Endocrine System Basic Definition Examples Diagrams




Biology Ii Lecture 3 The Endocrine System Flashcards Quizlet



Stream Exocrine Glands Marta Perez By Eva Kmi Listen Online For Free On Soundcloud



Exocrine Glands Youtube




Quick Answer Which Is The Largest Exocrine Gland In Human Body The Biggest
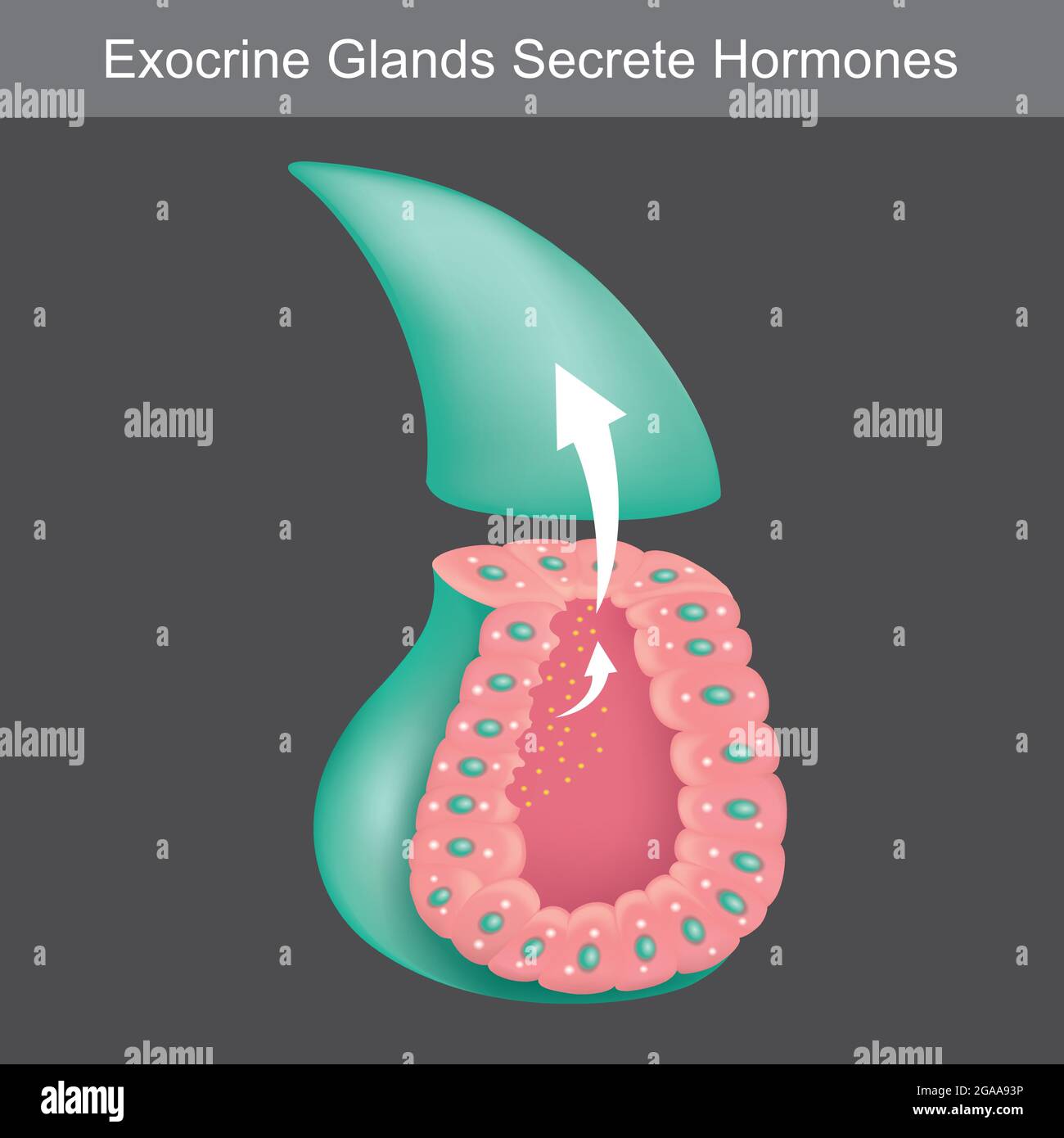



Exocrine Glands Secrete Hormones Illustration Showing Cross Section For Learning Exocrine Glands Human Stock Vector Image Art Alamy




Exocrine Gland Images Stock Photos Vectors Shutterstock




Differences Between Endocrine Glands And Exocrine Glands
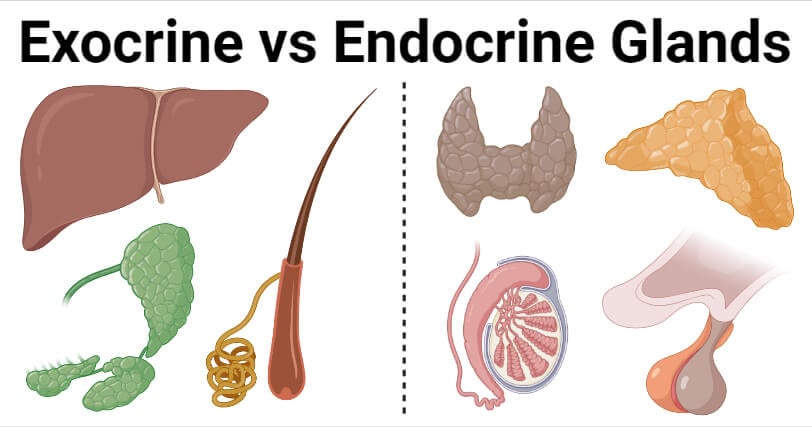



Exocrine Vs Endocrine Glands Definition 8 Differences Examples
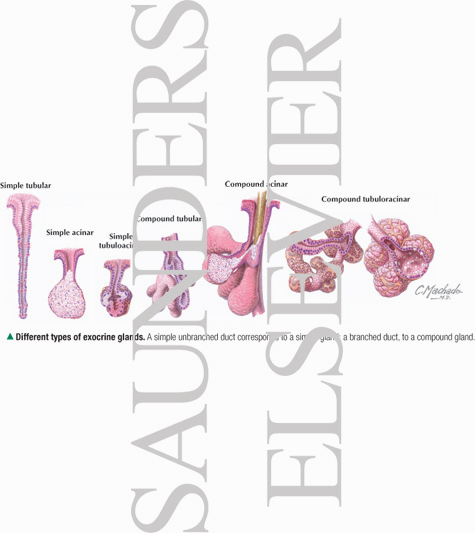



Different Types Of Exocrine Glands



Exocrine Glands
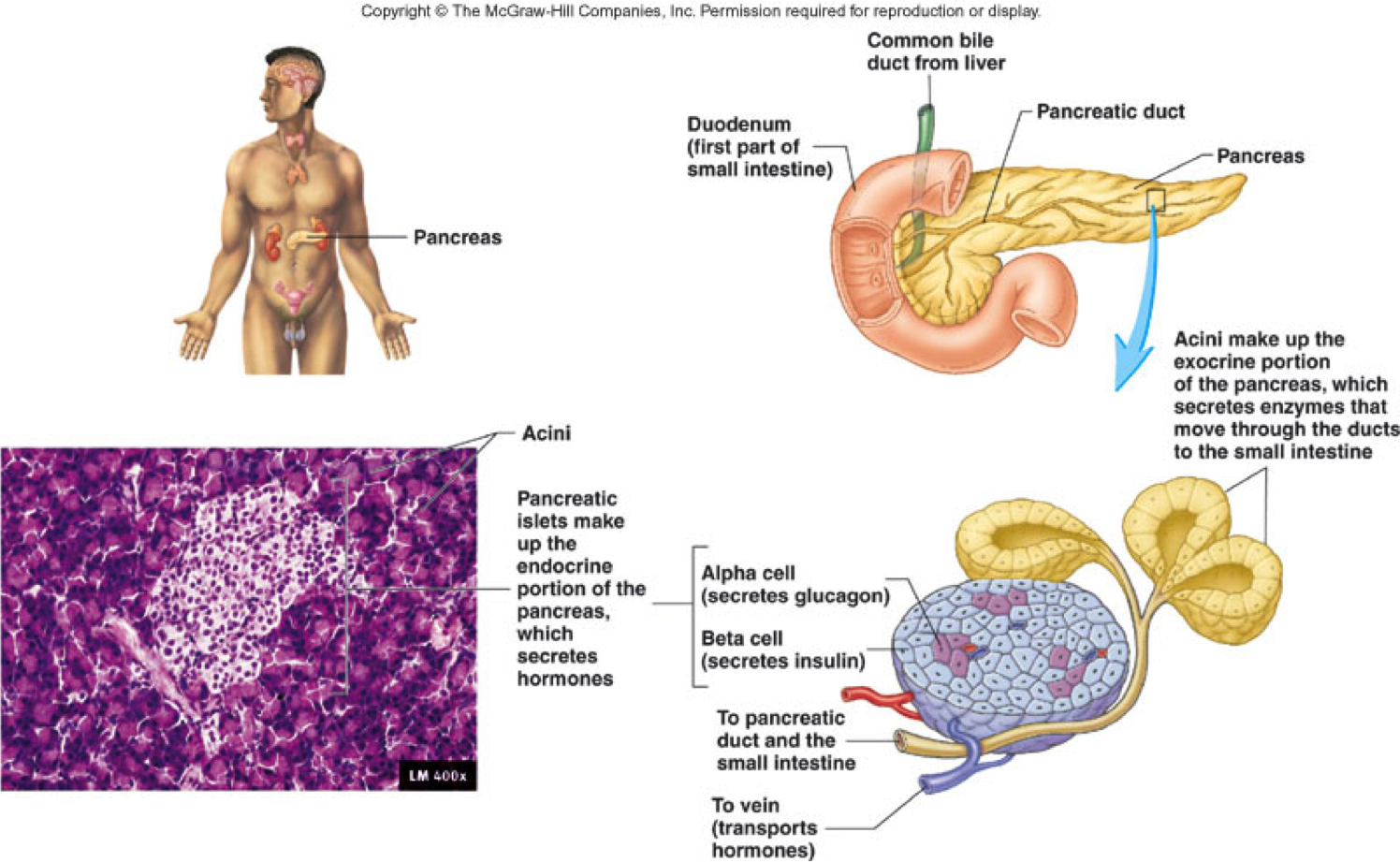



Do Any Of The Exocrine Glands Produce Hormones Socratic




Exocrine Glands Proceedings Of A Satellite Symposium Of The Xxiv International Congress Of Physiological Sciences Anniversary Collection Stella Y Botelho Frank P Brooks Amazon Com Books




Learn About Diagram Of Exocrine Gland Chegg Com



Difference Between Exocrine And Endocrine Difference Between




Exocrine Glands Bioninja




Pin On Part I Study Guide



2
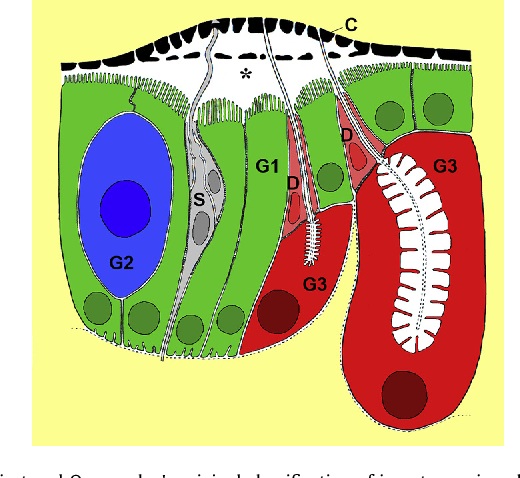



Pdf Insect Exocrine Glands Semantic Scholar




Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Differences Function Terms Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
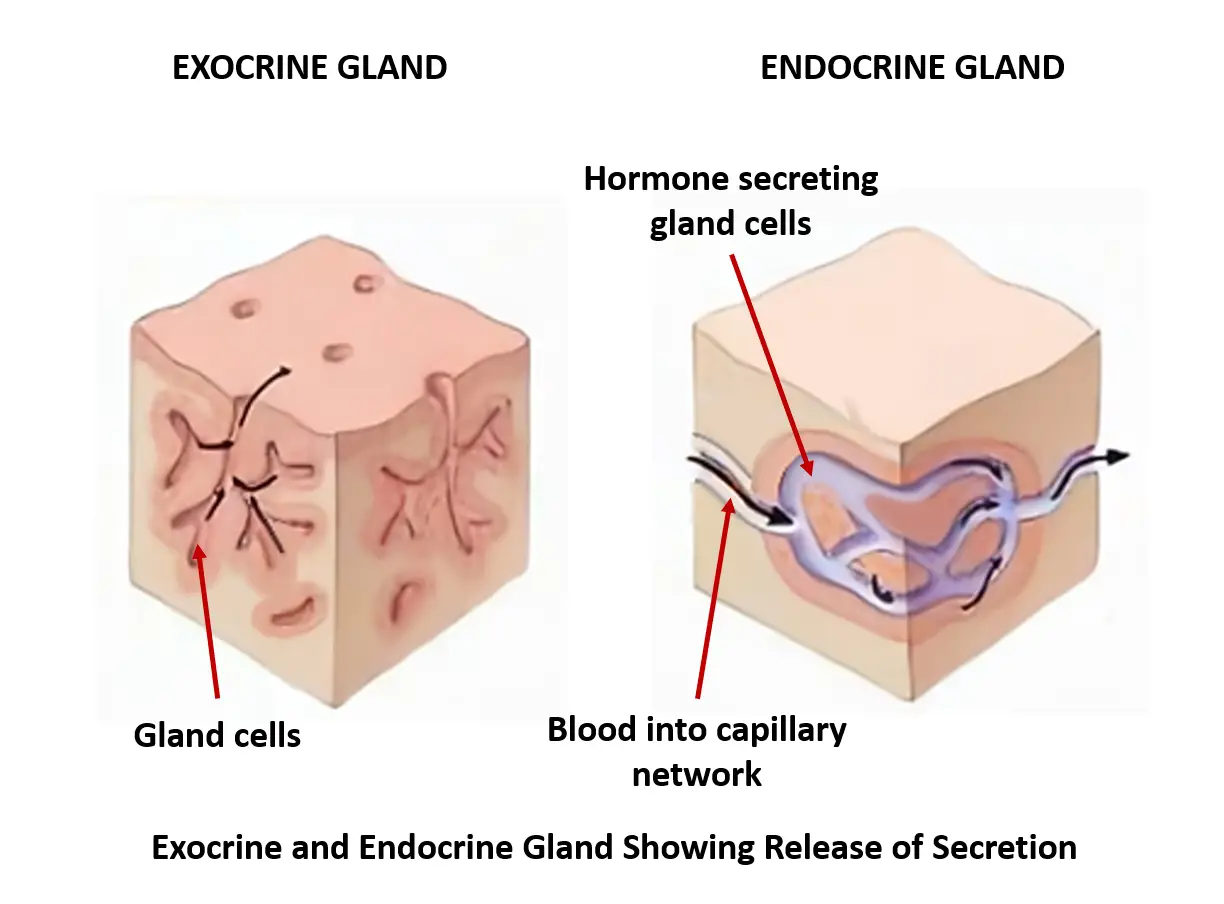



Exocrine Vs Endocrine What Is The Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine You Ask We Answer




Unlike Endocrine Glands Exocrine Glandsa Clutch Prep




Glands Hormones Oestrogen Glucagon Adrenaline Insulin Testosterone Syllabus




Exocrine And Endocrine Glands Royalty Free Cliparts Vectors And Stock Illustration Image
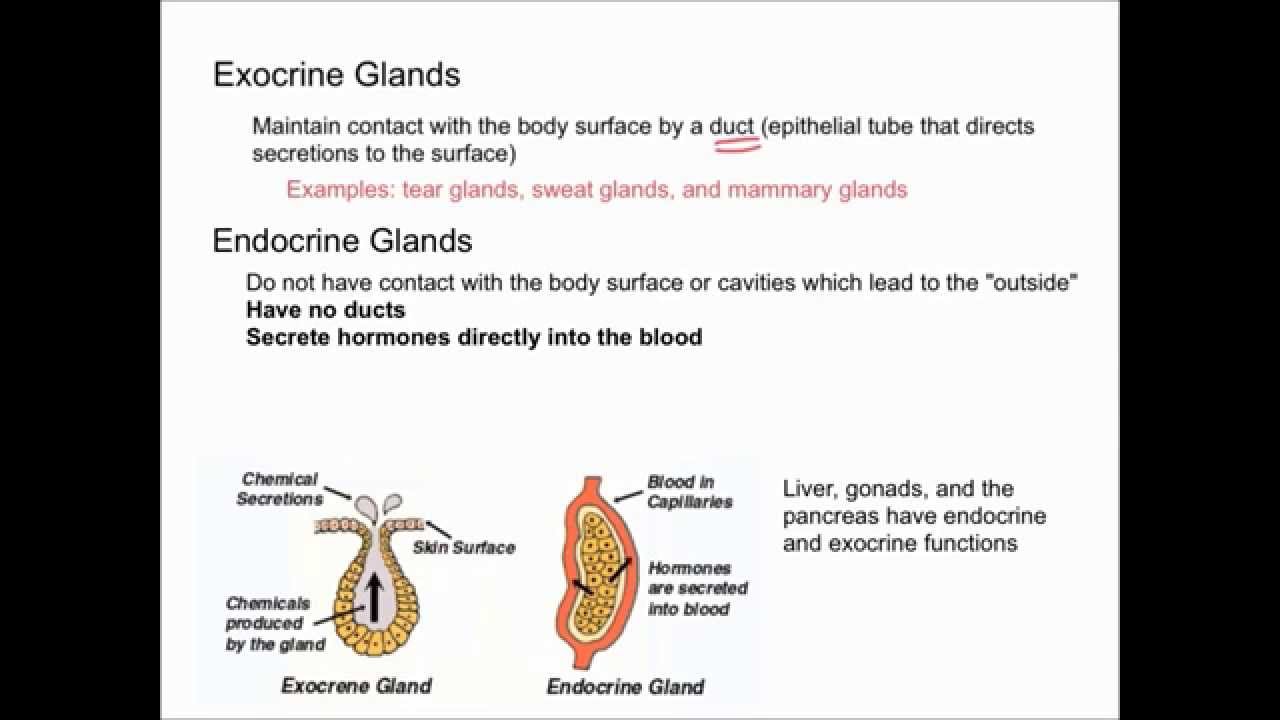



Endocrine Vs Exocrine Glands Youtube



Difference Between Endocrine And Exocrine Glands Difference Guru




Epithelial Tissues Exocrine Glands Quiz Digital Histology
コメント
コメントを投稿